SAP is one of the top ERP systems in the field of financial accounting. It makes it possible for businesses to effectively and precisely record all of their financial transactions. FB50 is one of the most often utilized transactions in SAP for journal entry publishing. It enables users to publish credit and debit entries straight to bank accounts and is utilized for manual journal entries.
It can be tiresome, nevertheless, to deal with repetitive journal entries. SAP has a feature called default values for FI posting in FB50 to help with this problem. By automatically filling in specific fields according to predetermined criteria, default values can streamline the process, minimize errors, and require less manual labor.
What is Transaction FB50?
- Journal entries are posted using the FB50 transaction in SAP’s Financial Accounting (FI) module. Typically, these journal entries are created to document routine financial transactions that are not picked up by automatic systems like payments or invoicing. The debit and credit amounts for different general ledger (GL) accounts can be manually entered by users using FB50.
Users can enter values in a number of fields in the transaction, including:
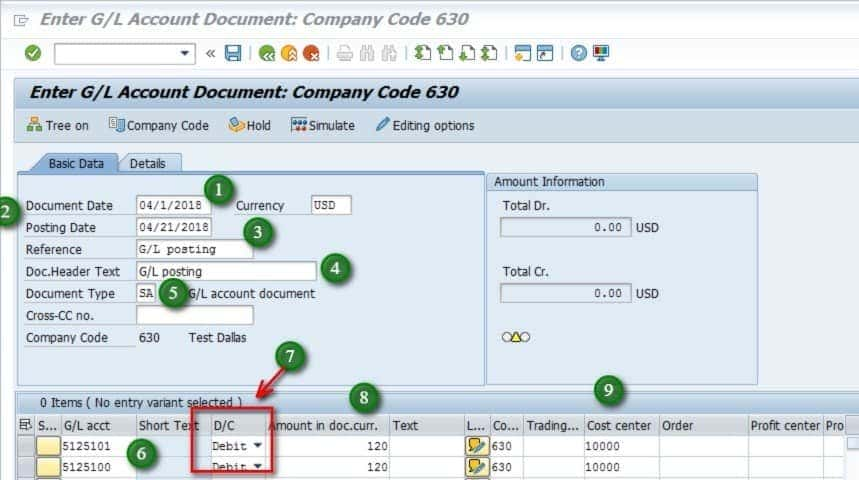
- Date of Document: The day the transaction took place.
- Posting Date: The date that the transaction is recorded in the accounting records is known as the “posting date.”
- Company Code: The unit of organization where the transaction is recorded.
- Currency: The money that was exchanged during the transaction.
- G/L Account: The credit or debit’s general ledger account.
What Are Default Values in FB50?
- Default values in SAP are preset values that minimize the need for human data entry by automatically filling up fields on transaction screens. SAP enables users to expedite the posting process by setting default values for specific fields in FB50. The business code, document type, or other pertinent factors can be used to determine these default settings.
- For example, you can set up specific accounts or cost centers to show up immediately when a new document is created if they are regularly used in journal entries. This can guarantee uniformity in financial reporting and greatly expedite the posting process.
Key Fields in FB50 and Their Default Value Settings
To improve process efficiency, default values can be defined in a number of crucial FB50 transaction fields:
- Date of Document : The date on the document indicates the time of the transaction. Depending on business needs, this may differ from the publishing date, which is typically the same.
The default value setting is: Depending on the requirements of the company, you can set the document date to default to either the current day or a specified date.
- Date of Posting : The accounting period in which the transaction is recorded is indicated by the posting date. Though it can occasionally differ, this is usually the same as the document date.
Default Value Setting: Either the posting period specified in the configuration settings or the current system date can be used as the default for posting dates. - Company Code : Company Code The SAP organizational unit that denotes a legal entity is called the company code. It serves to coordinate business-level transactions and establishes the financial structure.
The default value setting is: In order to guarantee that users automatically publish to the appropriate company code when creating journal entries, a default company code can be specified based on the user’s profile or department. - The G/L Account : The foundation of financial accounting is the general ledger account, or G/L account. All financial transactions are tracked with it.
The default value setting is: Depending on the document type or cost centers, default G/L accounts can be configured for specific transactions, including common expenses or income entries. - Quantity : The value of the transaction being posted (either credit or debit) is shown in the amount column.
The default value setting is: SAP enables the setting of default amounts depending on specific criteria, such as vendor, customer, or document type, even though the amount is normally entered manually. - Center of Cost : The department or unit in charge of incurring the costs is referred to as the cost center. Internal reporting and control both benefit from it.
Default Value Setting: To prevent tedious data entering, this can be pre-configured if specific departments regularly publish to the same cost center. - Money : The currency in which the transaction is posted is specified in the currency field. Depending on the transaction, this could be the local currency of the company code or a foreign currency.
The default value setting is: When handling multi-currency transactions, accuracy can be guaranteed by setting the currency field to default depending on the document type or business code.
How to Set Up Default Values for FB50
- SAP allows system administrators or consultants to configure default values for various fields in FB50 through several approaches. The process usually involves customizing settings via transaction codes or configuration menus.
Step 1: Define Default Values in the SAP System
To set default values for FB50, you typically need to access the Customizing settings in SAP. This can be done using the transaction code SPRO.
- Navigate to SPRO: Enter transaction
SPROand click on SAP Reference IMG. - Financial Accounting Configuration: Under Financial Accounting, go to General Ledger and then select Master Data or Document Posting.
- Define Document Types and Posting Rules: Here, you can define the document types, account types, and the corresponding default values for fields such as G/L account, cost center, and currency.
Step 2: Default Values for Users or Roles
SAP allows you to set default values based on user roles or profiles. For instance, if a particular user often posts entries for a specific department or business unit, their default values can be configured accordingly.
- User-Specific Defaults: Navigate to the User Profile settings in SAP (via transaction
SU01). - Assign Default Values to Fields: For each user, assign default values for commonly used fields (e.g., cost center, G/L account).
Step 3: Maintain Cost Centers and G/L Accounts for Default Assignment
Cost centers and G/L accounts can be maintained via Master Data in SAP. By associating these with the relevant document types, SAP can automatically suggest default entries when a user posts a journal entry.
Benefits of Using Default Values in FB50
There are various advantages to using default values for FI postings in FB50.
1. Effectiveness and Rapidity
- By automating repetitive tasks, default values drastically cut down on the amount of time needed to post journal entries. For departments like finance or accounts payable that regularly post similar data, this is extremely helpful.
2. Error Mitigation
- The likelihood of making mistakes (such publishing to the incorrect G/L account or utilizing the incorrect cost center) is reduced by pre-populating fields with default values. As a result, financial reporting and compliance are improved.
3. Consistency
- Default values help maintain consistency in data entry, ensuring that all users follow the same set of procedures and rules. This standardization is critical in large organizations with many users posting financial transactions.
4. Improved Reporting
- Default values ensure that the correct fields are populated consistently, making it easier to generate accurate financial reports. Properly configured defaults reduce the need for manual adjustments or corrections in the reporting phase.
5. Customizable for Business Needs
- Default values can be customized to align with the unique needs of an organization. Different users, roles, or departments can have different default settings, making the system flexible and adaptable.
Conclusion
- One essential tool for submitting journal entries in SAP is the FB50 transaction. Organizations can guarantee consistency in financial transactions, minimize errors, and expedite the posting process by utilizing default values. Businesses can improve overall financial processes and increase efficiency by setting default values for a variety of fields, such as currency, cost center, and G/L account. In addition to saving time, putting these defaults into place guarantees financial reporting accuracy and compliance.
- Knowing how to configure and apply default values in FB50 will greatly improve your company’s SAP Financial Accounting procedure if you are a SAP consultant or user. Achieving financial transparency and preserving seamless operations depend heavily on the advantages of automation, precision, and personalization.
you may be interested in this blog here:-
Top SAP Modules in Demand 2024 Insights & Trends
Advanced OOP Concepts in SAP ABAP A Comprehensive Guide
GRC Security: Ensuring Comprehensive Governance, Risk, and Compliance







