Introduction Generative AI for Maximum Impact
Generative AI for Maximum Impact: When touch screens were first seen in Star Wars in the 1980s, it was a fantasy, but today, they are a part of our everyday lives. Who would have imagined a bomb that fits in a hand would reduce a whole city to ashes, or computer intelligence would reduce the menial jobs done by humans? Fast forward to the last four decades, and we see a lot of things that people could have only imagined but have become our reality. However, two things termed “The next big thing” have stood out. The Splitting of an Atom and Artificial Intelligence. These discoveries have changed our lives to a large extent. Let us focus a little more on Artificial Intelligence. You would be surprised to know that a survey in the US showed that Gen AI had a steeper initial adoption curve than the other recent technologies. Below is the graph showing the same:
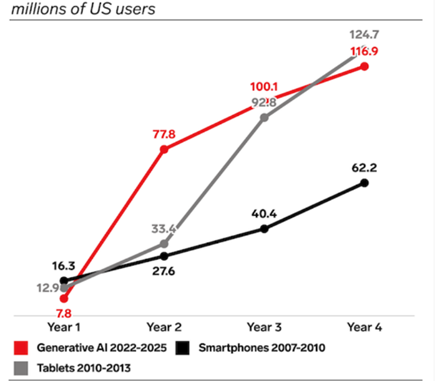
Figure 1: Generative AI has a steeper Initial Adoption Curve than Other Recent Technologies,
Generative AI adoption climbed faster than smartphones, tablets, Sara Lebow, Insider Intelligence, August 11, 2023: https://www.insiderintelligence.com/content/generative-ai-adoption-climbed-faster-than-smartphones-tablets
Another interesting fact is the rate at which it is being adopted in different industries in the United States in 2023, shown below:
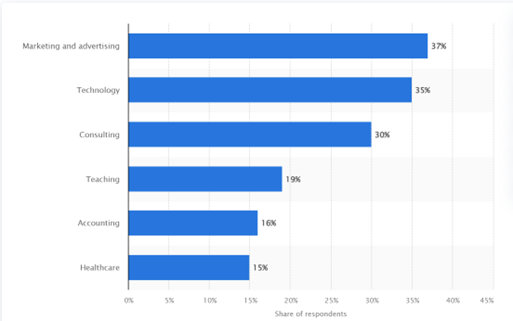
Figure 2: Rate of Generative AI adoption in the workplace in the United States 2023, by industry,
Generative AI adoption rate at work in the United States 2023, by industry, Bergur Thormundsson, Statista, December 5, 2023: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1361251/generative-ai-adoption-rate-at-work-by-industry-us/
Before we dive deep into all this, let us first understand what artificial intelligence is. Artificial Intelligence (AI) was first stumbled upon in the 1950s during the Turing test when the traditional AI or weak AI was born. Computers can perform tasks that need human cognition.
Traditional AI
In essence, traditional AI involves programming a machine to follow predetermined guidelines to produce a specific result. It is less human-like since it cannot complete a task independently and cannot function without set rules. Traditional artificial intelligence does have many uses in daily life. For example, spam filters separate unsolicited emails based on recommendation algorithms, and virtual games like chess, with pre-programmed tactics, work well on smartphones. Virtual assistants like Siri, Cortana, or Alexa use Traditional AI and have predefined algorithms. These algorithms allow them to perform specific tasks or answer questions in a particular manner.
Generative AI
Generative AI essentially leverages neural network techniques to extract patterns and structures from massive datasets. They help generate new content, such as texts, photos, music, and videos, to mention a few. These days, ChatGPT and BARD are widely discussed. People use them for various tasks, from writing an essay or a code for a particular program to forecasting an outcome or proposing a hypothetical solution.
A mother in the US recently utilized ChatGPT to diagnose her son’s illness. She was shocked to learn that ChatGPT correctly identified what 17 of the world’s best doctors could not diagnose.
Let us understand how Generative AI is transforming our lives and what the advantages of using Generative AI are.
Enhance customer experience: Increasing customer satisfaction is a noteworthy application of generative AI. Businesses can improve customer engagement by deploying dynamic AI agents that can provide human-like responses to consumer inquiries.
Hyper-personalization: Generative AI can hyper-personalize the consumer experience by analyzing customer data and generating customized product recommendations and offers based on individual preferences.
Customer support: In contrast to monotonous, identical-sounding robotic voices, voice automation can enable brands to provide customer support in dynamically changing, personalized voices. It reduces customer frustration and enhances the human likeness and naturalness of interactions.
Creativity amplification: Thanks to generative AI, businesses can create engaging content on a large scale. AI-powered systems have the potential to generate effective ad language, images, and video content automatically in the advertising sector. This could be a valuable tool for generating creative ideas and reducing the need for manual creative effort.
Time and cost savings: By automating tasks that previously required human intervention, generative AI reduces costs and saves time. For example, AI algorithms may generate building designs based on given parameters in architecture and design, considerably speeding up the design process.
Enhanced efficiency and productivity: Businesses can automate labor-intensive, complex processes with generative AI. In the industrial sector, AI algorithms may generate effective production schedules that lower waste and increase productivity.
Data synthesis: One promising area for generative AI applications is data synthesis. AI models can use their ability to analyze various datasets to synthesize enormous amounts of data and generate insightful information. For example, generative AI in the financial sector may assess economic data, consumer behavior, and market trends. This can be used to create prediction models that assist firms in making informed investment decisions.
Realistic simulations: Generative AI can be used to create realistic simulations that can be used in a range of settings for research, education, and entertainment. In the automotive industry, AI-powered simulators can accurately replicate driving conditions, making autonomous car testing safer and more efficient.
Generative AI industrial applications are plentiful
Logistics and transportation: This industry can utilize Gen AI to navigate new areas by converting satellite images into map views.
Travel: Generative AI can help create a comprehensive image from different photos to identify and verify a traveler’s identity.
Healthcare: In the healthcare industry, generative AI can turn electronic health records into risk predictors, identifying risks of antibiotic resistance, drug doses, and infection patterns. It can also help to train medical professionals using virtual reality by simulating realistic and accurate procedures.
Retail: Using token size, previous purchases, purchase patterns, and other pertinent data, generative AI can personalize messages and emails with products relevant to prospective customers.
Supply chain: Demand analysis using generative AI can help reduce waste and overstocking. As a result, profit margins and inventory costs are lowered.
Energy sector: Based on meteorological data and production history, predicting solar and wind output can be used to manage resource variability and optimize grid integration. Additionally, generative AI can help optimize power transmission and distribution while accounting for load balancing, traffic control, and asset utilization.
Marketing and advertising: Generative AI can be used for targeted advertising, digital advertising, and sentiment analysis, thus helping both industries.
Although there are many advantages and industrial applications for generative AI, at this nascent stage, it also has certain limitations, as mentioned below:
- Accurate responses necessitate many data points and processing power, which means additional infrastructure is needed.
- Quality checks are necessary because the quality of the generated data is not constant.
- A greater chance of cyberattacks spreading false information entails sophisticated cybersecurity measures to lower this risk in the future.
- Although generative AI is still in its infancy, it will eventually develop the ability to deal with moral and emotional quandaries.
Conclusion
Since society is changing so quickly, nothing in this world is inevitable. However, generative AI seems to be a step towards more advanced AI or digital technologies that will drastically change how we live today. However, one thing is sure: generative AI will persist.