Introduction
Since they enable the rectification of financial errors without changing the original transaction data, reversal papers are crucial parts of any ERP system, but they are especially important in SAP. These records offer a reliable audit trail, preserve data integrity, and guarantee transparency. The various reversal document kinds that SAP offers, their functions, and the best ways to use them will all be covered in this article. You will have a comprehensive grasp of how reversal documentation can increase accuracy and expedite financial procedures in your company by the conclusion.
What Are Reversal Documents?
- To reverse or cancel financial transactions that were recorded improperly or require modifications, reversal papers are prepared in SAP. SAP generates a new document that reverses the consequences of the original entry rather than altering or removing the old transaction directly. This method offers a visible means of tracking corrections and guarantees data integrity.
Why Are Reversal Documents Important?
- Audit Compliance: By displaying both the initial transaction and subsequent reversal, reversal documents produce an unambiguous audit trail.
- Data Integrity: Preserves the accuracy of records by preventing direct modifications to financial data.
- Error Correction: Error correction makes it easier to correct mistakes without compromising other entries.
- Regulatory Requirements: sists businesses in meeting financial and legal requirements.
- Streamlined Processes: Reduces manual error and saves time by automating and streamlining the reversal process.
Types of Reversal Documents in SAP
To address diverse situations, SAP provides a range of reversal document types. Let’s examine each kind in more detail:
1. Standard Reversal
- The most popular kind of reversal document is this one, which is used to reverse straightforward financial operations including payments, invoices, and journal entries.
Key Features:
- can be carried out with transaction codes such as F.80 or FB08.
- A reversal document with the opposite sign of the original entry is automatically created by the system.
Use Case: When the incorrect client account receives a payment.
2. Reversal with Clearing
- When a transaction is connected to another clearing document, this type is utilized. Correct updating of the clearing status is guaranteed by the reversal procedure.
Key Features:
- Both the original document and the clearing document that goes with it are reversed.
- keeps the cleansing procedure consistent.
Use Case: When an invoice was paid with the wrong payment.
3. Negative Posting Reversal
- This technique modifies the initial transaction without nullifying it by generating a reversal record with negative posts.
Key Features:
- permits edits while maintaining the original document’s functionality.
- requires the system’s negative posting feature to be activated.
Use Case: For correcting little mistakes in tax or discount computations.
4. Reversal in Controlling (CO)
- Internal cost accounting records, like cost center postings or internal orders, are the subject of reversals in controlling.
Key Features:
- used transaction codes such as KB41N or KB11N.
- guarantees proper reporting of internal costs.
Use Case: When expenses are inadvertently recorded to the incorrect cost center.
5. Partial Reversal
- With this kind, only a section of the original document can be reversed instead of the complete thing.
Key Features:
- allows for certain changes to be made without affecting the entire transaction.
- beneficial for intricate financial records with several line items.
Use Case: When an invoice just has to have one line item corrected.
6. Mass Reversal
- Mass reversal is used to reverse several papers at once, as the name implies.
Key Features:
- carried out with transaction codes such as FBRA.
- When handling large corrections, it saves time.
Use Case: When a systematic error causes many payments to be made to the incorrect account..
7. GL Account Reversal
- Reversing General Ledger entries is the main goal of this type.
Key Features:
- used exclusively for GL postings.
- aids in keeping ledger balances accurate.
Use Case: When the wrong GL account is impacted by an inaccurate journal entry.
8. Accrual and Deferral Reversal
- used at the conclusion of a period to reverse accrual or deferral postings.
Key Features:
- uses predetermined reversal dates to automate reversal.
- simplifies closing tasks at the conclusion of the period.
Use Case: When accruals for pre-paid charges are reversed.
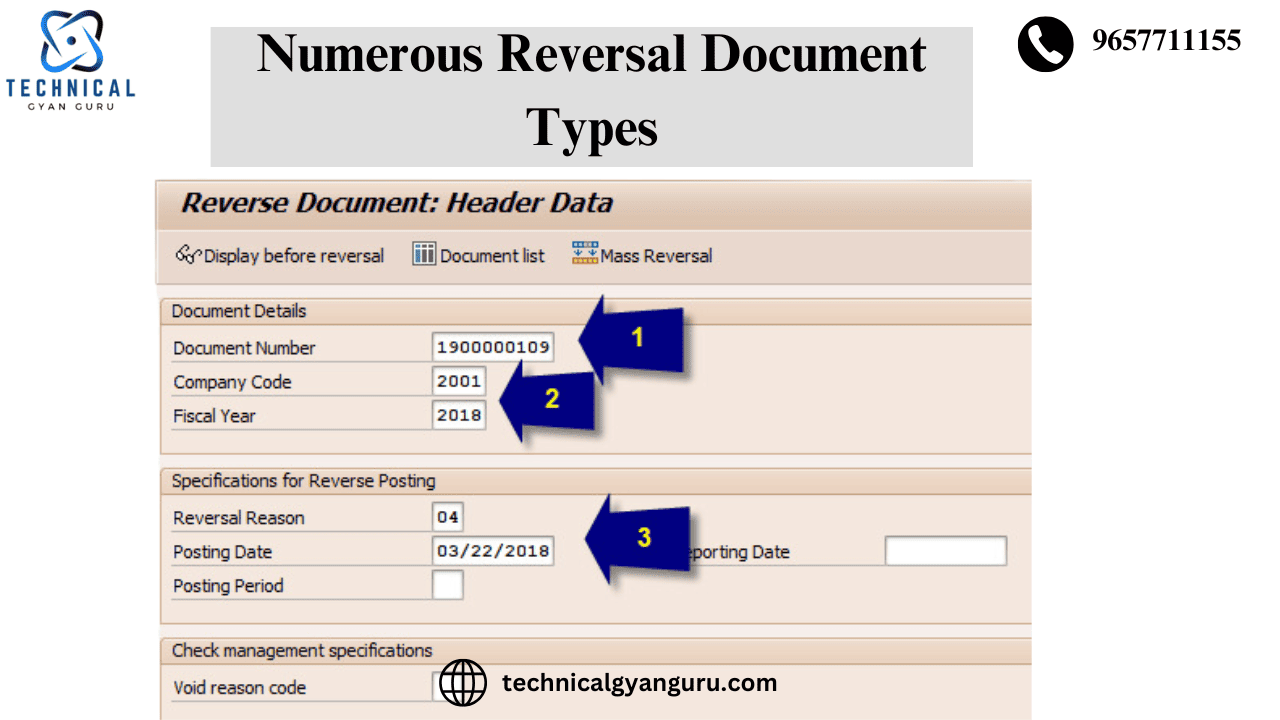
Steps to Perform a Standard Reversal in SAP
This is a brief summary of how to carry out a simple reversal in SAP:
- Access the Reversal Transaction:
- Use the transaction codes F.80 (Mass Reversal) or FB08 (Individual Reversal).
- Enter Document Details:
- Give the fiscal year and document number of the transaction that has to be reversed.
- Select Reversal Reason:
- From the predetermined list, select the proper reversal cause.
- Execute the Reversal:
- To finish the reversing procedure, click “Post”.
- Verify the Reversal Document:
- To verify the reversal, look at the reversal document in the document display (FB03).
Best Practices for Using Reversal Documents
- Define Clear Reversal Reasons:
- To guarantee appropriate documentation, keep an exhaustive list of reversal causes.
- Restrict Authorization:
- To avoid abuse, restrict reversal permissions to authorized workers only.
- Double-Check Before Posting:
- Before starting a reversal, always double-check the original document details.
- Use Negative Postings Wisely:
- To prevent inconsistent data, only activate negative postings when required.
- Reconcile Regularly:
- At period-end close, make sure all reversal papers are reconciled.
- Audit Reversal Processes:
- To make sure that organizational policies are being followed, conduct audits on a regular basis.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
1. Incorrect Reversal Reasons
- Solution: The answer is to teach consumers how to choose the right reversal arguments.
2. Authorization Issues
- Solution: Configure reversal transactions with role-based permissions.
3. Impact on Financial Reports
- Solution: To prevent reporting inconsistencies, use reversal documents within the same fiscal period.
Conclusion
- Reversal documents are essential resources for preserving SAP’s financial integrity and accuracy. Organizations can guarantee compliance, speed error correction procedures, and preserve an open audit trail by knowing the various kinds of reversal papers and their applications. The efficiency of reversing papers in your SAP system can be further increased by adhering to best practices and resolving typical issues.
- Reversal papers give you the flexibility and control you need to maintain the accuracy and dependability of your financial data, regardless of how simple or complex the error is.
you may be interested in this blog here
Building Interactive Forms with Adobe LiveCycle Designer
oracle dba architecture interview questions







