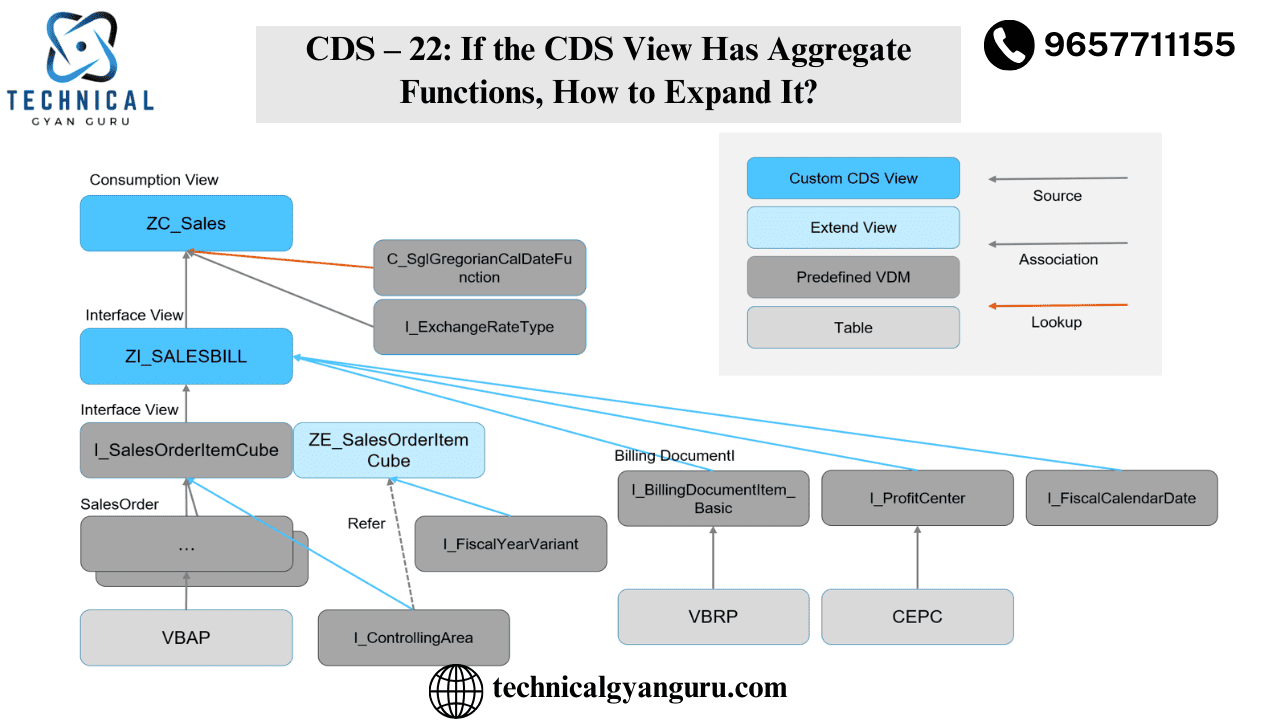
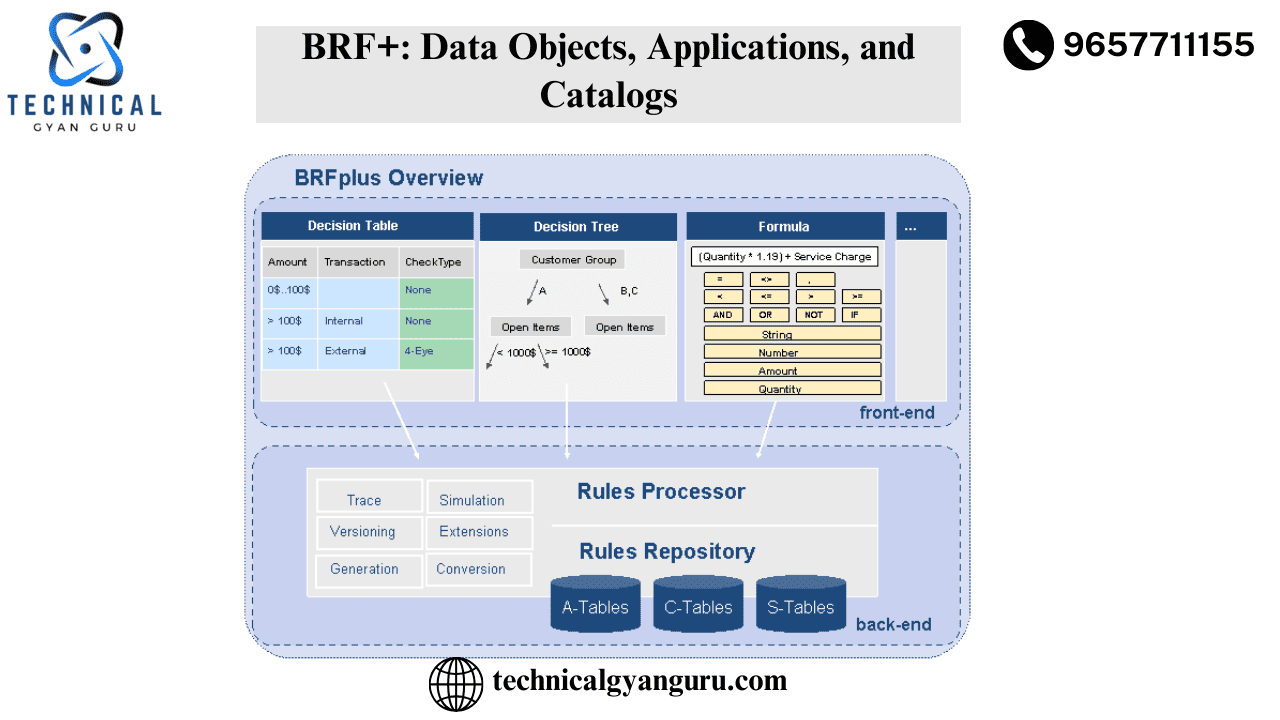
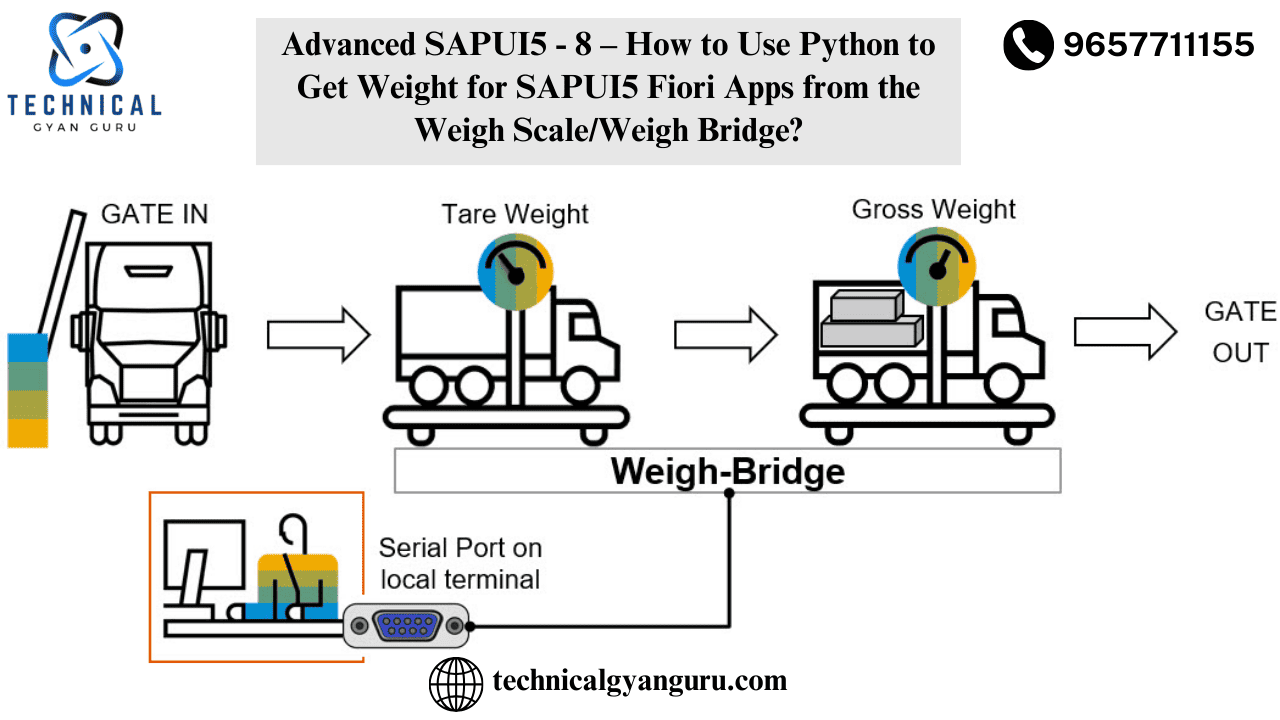
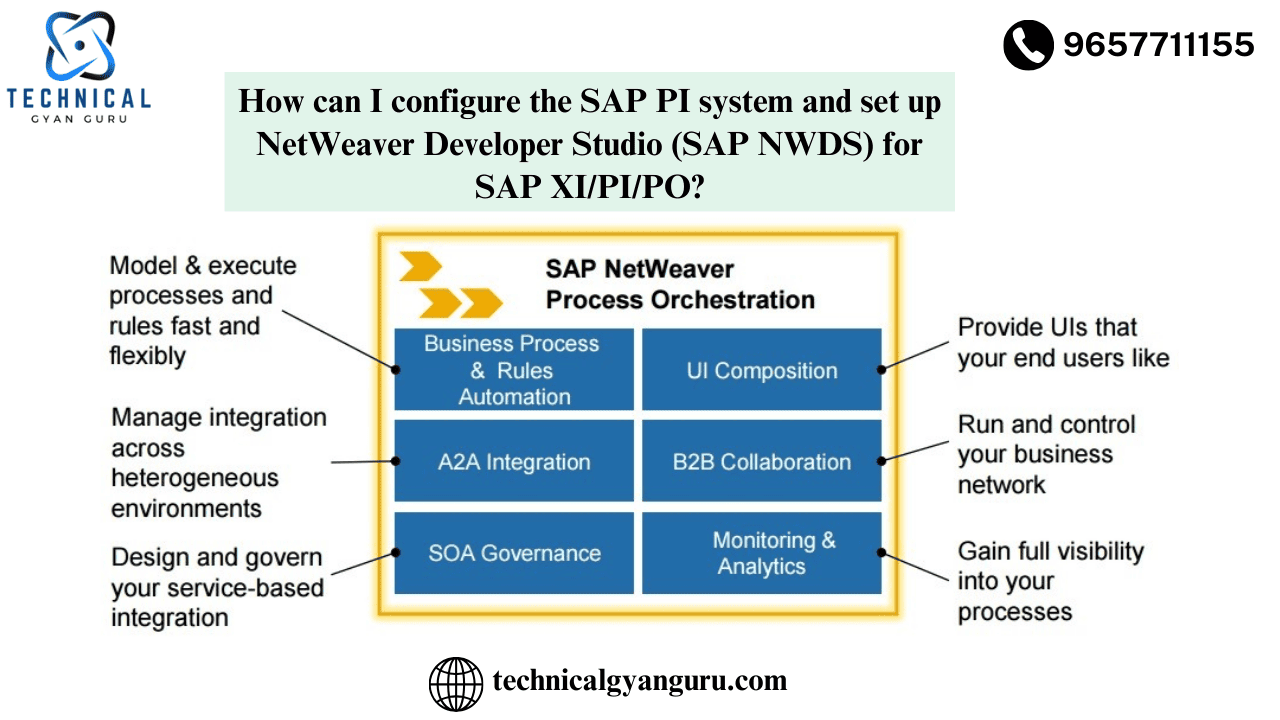
Introduction: Basics of SAP MM
Basics of SAP MM: In the ever-evolving landscape of enterprise resource planning (ERP), SAP MM (Material Management) stands out as a crucial module that plays a pivotal role in streamlining and optimizing the procurement and inventory processes of organizations. In this blog post, we will delve into the fundamentals of SAP MM, exploring its key features, functionalities, and significance in the realm of business operations.
Understanding SAP MM:
SAP MM is a module within the SAP ERP system that focuses on managing materials and resources within an organization. Its primary objective is to facilitate the procurement and management of materials, ensuring a seamless flow of goods and services. The module covers a wide range of functions, from the initial procurement of materials to their storage, consumption, and eventual disposal.
Key Components of SAP MM:
- Master Data:
- Material Master: Contains information about all materials used in the production and distribution processes.
- Vendor Master: Stores details about the suppliers and vendors from whom materials are procured.
- Procurement:
- Purchase Requisition: Initiates the procurement process by requesting the purchase of materials or services.
- Purchase Order: Formalizes the purchase, specifying the details of the materials, quantities, and delivery dates.
- Goods Receipt: Records the receipt of materials, updating the inventory and triggering the payment process.
- Inventory Management:
- Goods Issue: Documents the withdrawal of materials from inventory for consumption or production.
- Stock Transfer: Facilitates the transfer of materials between different storage locations within the organization.
- Valuation and Account Determination:
- Determines the value of materials in inventory and the corresponding accounting entries.
- Invoice Verification:
- Matches invoices from suppliers with purchase orders and goods receipts, ensuring accuracy before payment.
- Material Requirement Planning (MRP):
- Forecasts and plans the materials needed for production based on demand and existing inventory levels.
Benefits of SAP MM:
- Enhanced Efficiency:
- Streamlines procurement processes, reducing manual efforts and minimizing errors.
- Provides real-time visibility into inventory levels, aiding in effective decision-making.
- Cost Savings:
- Optimizes procurement processes, negotiating better terms with suppliers and minimizing excess inventory.
- Accurate Financial Reporting:
- Integrates seamlessly with other SAP modules, ensuring accurate and up-to-date financial reporting.
- Compliance and Risk Management:
- Helps organizations adhere to regulatory requirements and mitigate risks associated with procurement and inventory management.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, SAP MM is the backbone of efficient material management in organizations, providing a comprehensive solution for procurement, inventory management, and related processes. By leveraging the capabilities of SAP MM, businesses can achieve greater operational efficiency, cost savings, and improved decision-making, ultimately contributing to their overall success in a competitive market. As organizations continue to embrace digital transformation, SAP MM remains an indispensable tool for effective material and resource management.