Introduction
In order to ensure proper bookkeeping and transparency in financial records, accounting reversal entries are an essential instrument in financial management. Accounting errors are unavoidable, and reversal entries provide a methodical approach to fixing errors without changing the underlying transactions. The idea of reversal entries, their importance, their operation, typical situation examples, and best practices for their successful implementation will all be covered in this extensive book.
What Is an Accounting Reversal Entry?
A journal entry created to reverse the effects of a prior transaction is known as an accounting reversal entry. The reverse entry generates an offsetting transaction that negates the impact of the initial entry rather than erasing or changing the original transaction. For regulatory compliance and accurate financial reporting, this procedure guarantees data integrity and offers a transparent audit trail.
Why Are Reversal Entries Important?
- Error Correction: The most dependable method of correcting inaccurate postings or misallocations in financial records is through reversal entries.
- Audit Trail Maintenance: They provide accountability and transparency by keeping the original transaction intact.
- Compliance with Regulations: Keeping an accurate record of financial transactions is required by a number of accounting standards, including GAAP and IFRS.
- Simplified Adjustments: Reversals make repairs easier, particularly when month-end or year-end closing tasks are involved.
- Avoidance of Double-Posting: Organizations can reduce the possibility of duplicate transactions by reversing an inaccurate entry.
How Do Accounting Reversal Entries Work?
Reversal entries function by generating a new transaction that has the opposite outcome of the one that was created. For instance:
- The reversal entry will credit the same account if the original entry debited it, and vice versa.
- According to the organization’s policies, the reversal is frequently posted in the same accounting period or a later one.
Example:
- Original Entry: Instead of being credited to Advertising Expenses, a $1,000 expense is mistakenly debited to Office Supplies.
- Debit: $1,000 for office supplies
- Credit: Cash/Bank $1,000
- Reversal Entry: The wrong entry has been switched around.
- Debit: Cash/Bank $1,000
- Credit: Office Supplies $1,000
- Correct Entry: The right cost has been noted.
- Debit: Advertising Expenses $1,000
- Credit: Cash/Bank $1,000
Common Scenarios for Using Reversal Entries
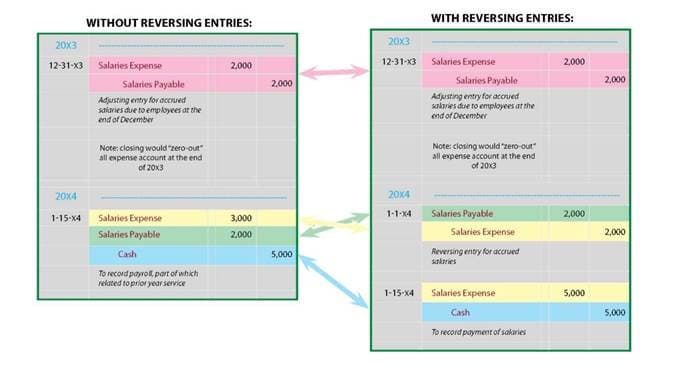
1. Accrual Adjustments
Accruals made at the end of a period are frequently reversed using reversal entries.
- Scenario: To represent the real payment, a $5,000 accumulated charge is reversed at the start of the following period.
2. Incorrect Allocations
A reversal can correct a transaction that has been posted to the incorrect account without affecting other records.
- Scenario: In error, a utility bill was charged to Repairs and Maintenance rather than Utilities.
3. Overstatements or Understatements
Reversals aid in correcting overstated or undervalued transactions.
- Scenario: A sales invoice that should have read $10,000 but was recorded at $12,000.
4. Voiding Payments
A reversal entry guarantees that the books show the correct cash position when a payment is canceled.
- Scenario: A system fault caused a customer payment to be input twice.
5. Intercompany Transactions
Reversal entries are frequently used to fix intercompany account mispostings.
- Scenario: The incorrect subsidiary was billed for an expense.
Steps to Create a Reversal Entry
1. Identify the Error
- Find the transaction that needs to be corrected.
- Check the information, including the date, amount, and account.
2. Create the Reversal
- To undo the impact of the initial transaction, post a journal item.
- Make sure the same accounts receive the reversal.
3. Post the Correct Entry
- To fix the mistake, record the right transaction.
4. Review and Reconcile
- To make sure the reversal and correction are accurately documented, reconcile the accounts.
- Check reports for accuracy.
Benefits of Using Reversal Entries
- Transparency: Keeps an accurate record of all adjustments.
- Efficiency: Makes fixing mistakes easier without interfering with other transactions.
- Better Reporting: Guarantees that accurate data is shown in financial reporting.
- Compliance: Complies with audit regulations and accounting standards.
- Flexibility: For quicker repairs, reversal entries can be automated in a number of ERP systems, including SAP and QuickBooks.
Challenges and Solutions
1. Frequent Errors Requiring Reversal
- Solution: To reduce errors, improve internal controls.
2. Complex Transactions
- Solution: To make maintenance easier, divide complicated transactions into smaller entries.
3. Timing Issues
- Solution: Clearly define guidelines for posting reversals and when to do so.
Reversal Entries in Popular Accounting Software
1. SAP
SAP uses transaction codes like FB08 to enable automatic journal entry reversal. It offers choices for scheduling reversals for a particular date as well as mass reversals.
2. QuickBooks
A straightforward interface for reversing journal entries is provided by QuickBooks. With only one click, users may find the original entry and produce a reversal.
3. Xero
For every reversed entry, Xero offers an audit trail, guaranteeing correctness and compliance.
Best Practices for Using Reversal Entries
- Establish Reversal Policies: Specify precise guidelines for when and how reversals must be carried out.
- Train Staff: Provide accounting teams with instruction on how to utilize reversal entries correctly.
- Leverage Automation: To reduce human mistake and automate the reversing process, use ERP systems.
- Audit Frequently: Make sure all reversals are appropriately documented and justified by conducting audits on a regular basis.
- Employ Descriptive Narratives: Give thorough explanations of the correction’s justification in reversal entries.
Conclusion
Maintaining correct financial records requires the use of accounting reversal entries. They offer a methodical and open approach to error correction while maintaining the original data’s integrity. Organizations may manage financial adjustments and guarantee accounting standards compliance by knowing their purpose, use cases, and best practices. Reversal inputs streamline the procedure and increase overall financial correctness, regardless of the complexity of the adjustments or the basic errors being handled.
you may be interested in this blog here:-
How Many Employees Does Salesforce Have in 2024?